All about Search Engine Optimization (SEO) in 2024
In this guide, Brandfirm breaks down everything you need to know, in uncomplicated terms, about Search Engine Optimization in 2024. With this guide within reach, Search Engine Optimization is made simple.

After reading this article, you learned:
- How search engine optimization contributes to a higher position in Google
- The three main pillars of search engine optimization
- How to pass your competitors in Google and generate more sales
- The search engine optimization trends for 2023
In this article
1. What is SEO?
Simply put, search engine optimization is optimizing your website to get a higher position in Google.
To illustrate: suppose you have a beautiful website or webshop.
You surely want as many people as possible to find your website or webshop.
Or better yet, take the next step. Like buying a product, for example. Or requesting a quote.
Search engine optimization increases the chance that this will happen.
To lead in Google, you need to optimize your content for the search engine.
This is done by using keywords that match your site. When visitors type those keywords into a search engine, they come across your company.
The SERP (Search Engine Results Page) will show your company’s webpage. At least, that's the goal.
And that's what happens when you optimize your website.
In short, you can't overlook search engine optimization as part of your online marketing strategy.
Request our free SEO analysis
- Gain insight into opportunities for SEO
- This takes us at least 4 to 6 hours of work
2. The benefits of search engine optimization
We just explained that search engine optimization is important for ranking higher in search results.
This, in turn, ensures that more people find your website in the SERP.
That is, search engine optimization ensures better visibility.
But there are even more benefits of SEO:
- A higher search engine ranking brings more traffic (so more visitors) to your website.
- SEO also increases conversion because you're optimizing your website.
- If you keep on track with your SEO, you’ll get long-lasting results.
- With search engine optimization, you don't need to generate a need. Instead, people come to you with their needs.
- Search engine optimization brings in relevant visitors.
3. How do search engines work?
We've established what SEO is and what the benefits are.
But to understand search engine optimization fully, you need to know how search engines work.
We're going to tell you all about that based on 4 steps.
Step 1: Crawling
An odd term, but crawling means that Google walks or 'crawls' through your website.
This is how, by jumping from link to link, the search engine discovers new content. Think of pages, images, videos, or PDF documents.
The more content, the more Google is able to 'crawl'.
Moreover, if you're considered to have a high level of authority (see Chapter 4), you’ll be crawled more often or for longer periods of time.
Step 2: Rendering
Next up, Google is going to render your website.
Rendering is the process where Google retrieves a page's HTML, JavaScript, and CSS resources and converts them into a graphically easy-to-understand image for your visitor.
This allows Google to figure out everything that's going on on your website. After this, your website is indexed.
It's good to know that a page can be indexed even if rendering has not yet taken place. Rendering can take place after indexing.
In the next paragraph, we'll tell you more about indexing.
Step 3: Indexing
Usually after rendering, indexing takes place.
This is basically a more complex term for registering. Indexing refers to registering your pages.
It's worth noting that this doesn't happen every day. So it may take a while before your pages are (re)indexed.
Only after your website has been indexed will it appear in the search engine results. That's why it's essential to index a website.
Only after that, it can be ranked.
Step 4: Ranking
Ranking follows after indexing.
This is the last step on your way to appearing in the search results.
Through ranking, a search engine gives you a position in the search results. This could be spot number one, or somewhere on the fifth page.
Spoiler: you don't want the latter. Because the higher your position, the more likely you are to convert visitors to readers.
In sum, the root of search engine optimization lies with the search engine itself.
But there are also 3 key pillars that define search engine optimization.
We’ll share these with you next.
Request our free SEO analysis
- A free analysis worth 4 to 6 hours of work
- 87% of the companies we analyze miss out on sales
4. The 3 pillars of search engine optimization
Simply put, SEO is made up of 3 pillars:
- Content optimization
- Technical optimization
- Link building
The latter is also known as 'authority.'
In this chapter, we'll explain what these 3 search engine optimization pillars are all about.
We'll also explain how to apply them to your website.
Let's start with the first search engine optimization pillar: content optimization.
Pillar 1: Content optimization (on-page SEO)
The name already gives it away, but content optimization covers all the content on your website.
This is also known as on-page SEO.
It's about everything you can see with the naked eye.

It's important to know that content should match visitors' search queries. This may sound a little vague. But we’ll make this easier for you with the help of a practical example.
Visitors and keyword research
Are you beginning to optimize the content on your website?
Then it's best to do some keyword research beforehand. This is also called keyword analysis.
This will help you understand which keywords and search terms to use.
This is necessary to attract the right visitors to your website.
Example
Take, for example, a webshop selling jewelry.
Your keyword analysis showed that people use the search term 'gold necklaces' a lot.
In that case, you need to incorporate this search term into your website.
This way, the search engine will know that your website is relevant to the visitor.
As a result, the search engine gives you a higher ranking. This in turn causes the user to land on your page.
And hopefully, this visitor will turn into a customer buying a gold necklace.
We've established that keyword research is what helps you find the right keywords. Next, it's critical to use keywords and search terms effectively on your website.
This has everything to do with the structure of your content. By this, we mean paragraphs and (sub)headings.
These are also called HTML headings.
HTML headings
A text without paragraphs, whitespace, or headings won't work.
The visitor can't properly scan your text. At the same time, the search engine will not like your website either.
Therefore, it's a must for search engine optimization to have a good layout.
A text always consists of HTML headings, such as H1, H2, and H3. It sounds complicated, but you can compare it to a book.
H1 is the title, H2 is a new chapter, and H3 is a subheading in that chapter. That's how the visitor dives deeper into the text.
HTML headings provide a logically structured layout.
The more elaborate the text, the more headings you need.

Is your paragraph too long? Then add a white line.
This way your paragraph remains readable and scannable.
Which is another major requirement for search engine optimization.
Featured snippet
Anyone using a search engine has probably seen them: a featured paragraph containing the answer to your search query.
These are featured snippets. You qualify for these by answering questions people are asking search engines, or in other words, optimizing your content for your target audience.
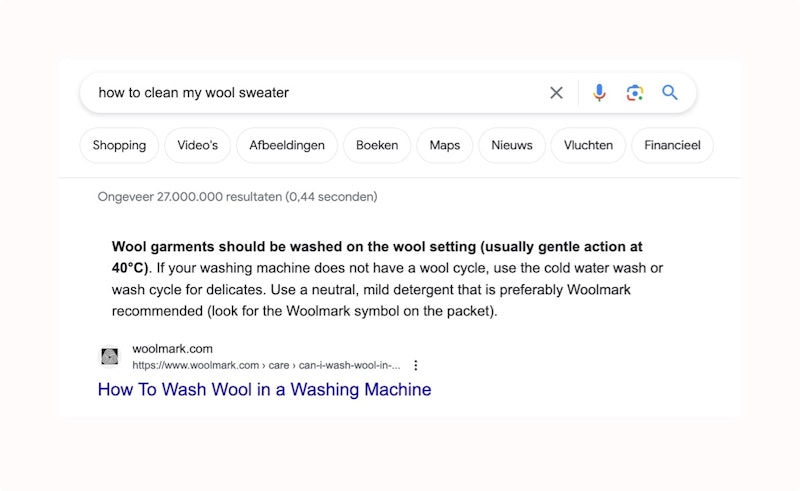
Write unique content
Optimizing content is not the only important thing. Writing unique content is also essential.
To this end, never copy texts from other websites or your own website. Otherwise, you'll have duplicate content.
This can negatively affect your position in Google's search results. If you steal content from another page, you might also be violating copyright laws.
The result can be a copyright infringement claim. So avoid this at all costs!
When writing your content, keep readability in mind. Don't write endless sentences, but keep them short and active. Signal words are also important.
Alt texts for images
In the previous paragraphs, we concluded that good content and structure matter.
But images are also part of your content. You can optimize these as well. To do this, adjust the alt text.
The alt text describes what is shown in the image. This is relevant for visually impaired people. They have the image read out loud.
In addition, the search engine will better understand what an image with alt text is all about.
Other things that fall under content optimization are:
- videos
- infographics
- social media buttons
- links
The collective term for this content is 'rich content.'
Personalize your meta tags
Meta tags are pieces of code in your HTML that determine how your website appears on Google.
Meta tags include meta titles and meta descriptions. But you can also modify these meta tags manually.
This way, you can personalize them for the user. The important thing is to label the keyword of your page.
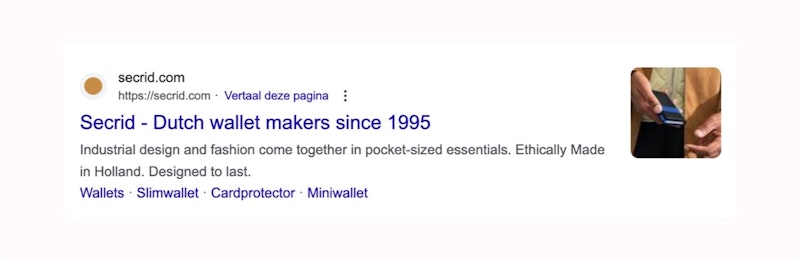
The meta title is the title of your page. This is the clickable link in the search results.
The meta description is the summary of the page. You can edit this one, too.
Summary
Content is not just the website’s text. It includes everything you see on a website. Content gives you a higher ranking and greater authority.
Content optimization includes:
- Doing keyword research for your target audience;
- HTML headings;
- Featured snippets;
- Unique content;
- Alt texts for images;
- Personalized meta tags.
But there are also plenty of aspects of search engine optimization that you can't see.
That's technical SEO. We'll cover this in the next chapter.
Pillar 2: Technical SEO
The second pillar of search engine optimization is technical SEO.
It refers to everything that happens on the back end of your website.
Technical SEO is important because it assures a good user experience. It also helps with faster indexing.
We'll explain what’s involved in technical SEO and how to optimize it in this chapter.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is a collective term for three metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- First Input Delay (FID)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
This sounds incredibly complicated.
But in a nutshell, it's how you measure the user experience by means of loading speed, responsiveness, and visual stability.
This might have to do with your website hosting. But it can also be related to your website's content.
In May 2024, Core Web Vitals became an essential baseline for Google. More on this in our subsection on trends for 2024.
Structured data
Structured data is where you add a piece of code to your content.
For example, Google understands that a 10-digit code is a phone number. Or that a street name with a number is an address. And so on.
You can do this by using schema.org language through JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa formats.
Canonical tag
Do you have an online shop and sell a product in different colors?
Then you probably have several pages with the same content.
After all, the product is the same, it just has different colors.
You can easily solve this by using a canonical tag. This tag tells Google that there’s one main page and the rest is part of it.
It will save you a lot of additional writing and duplicate content.
URL structure
Have you ever spotted a URL consisting of hundreds of numbers or letters?
Those URLs are not technically optimized. This is detrimental to your website's ranking.
Your website visitors also won’t understand where they're heading. Therefore, it's imperative to have a simple URL structure.
Think brandfirm.nl/en/search-engine-optimization. Chances are you'll immediately understand where the URL is taking you.
Responsive
One thing you should never forget is to make your website responsive (mobile-friendly).
After all, most people will visit your website on their mobile devices.
For this, your website should be set up differently than the desktop version. This means making texts readable and scaling images.
XML sitemap
Een XML sitemap is een overzicht van alle pagina’s.
Zo kan de zoekmachine zien hoe jouw website is opgebouwd.
Dit bevordert de indexatie en vooral het crawlen.
Caching
Caching is the temporary storage of data.
This helps with faster access to data.
A big advantage of caching is a fast load time.
Internal links
Embedding internal links into your text is hugely valuable.
Consider linking to one of your other blogs for more information. Or add a link to a contact page.
This way you're offering the reader more information on a particular topic. And you're helping the reader find the right page faster.
Using internal links also benefits your visibility. On the other hand, there are external links to other websites.
We'll discuss this in the chapter 'Link building.'
Summary
Technical SEO includes:
- Core Web Vitals to improve the user experience;
- Structured data to help Google understand (address) data;
- Canonical tags, which make sure identical pages are considered to be one page;
- A simple URL structure;
- A responsive website;
- XML sitemap, or an overview of all pages on your website;
- Temporarily storing data via caching;
- Internal links to find relevant pages faster.
After content optimization and technical SEO, we’re left with one more SEO pillar - link building.
We’ll cover this in the next chapter.
Pillar 3: Link building (off-page SEO)
The third and final pillar of search engine optimization is link building. This pillar is also referred to as 'authority.'
Link building is actively pursuing relevant and reliable external links.
External links are links from a website on another domain. These are called backlinks.
The goal of link building is to build a strong backlink profile to increase the authority of your website. A backlink profile is a collective term for all external links that link to your website.
The criteria for link building are:
- Relevance
- Reliability
- Authority
Consider carefully which external websites you want to link to and which websites link to your website.
If you use the wrong backlinks, it can affect the visibility of your website.
If you integrate the backlinks correctly, Google will consider you an authority. The result is a higher ranking.
The better the quality of your external links, the more authority you’ll get.
And that, in turn, is hugely positive for search engine optimization.
Receive our newsletter
- +5,000 entrepreneurs preceded you. We share our knowledge for free.
5. Local, regional, and international SEO
We’ve covered all three SEO pillars, including content optimization, technical SEO, and link building in the previous chapters.
However, there is a difference between local SEO, regional SEO, and international SEO. In this chapter, we'll go over these three SEO types.
We will tell you what they mean and which one is relevant to you.
Local SEO
It’s in the name: with local SEO, you can make your website or online shop easy to find on a local level.
And rightly so, because as many as 97% of people using Google look for a company or service in their area.
Besides that, local SEO has several other advantages:
- Local SEO increases your visibility among local customers;
- Because you're more visible, more people will click on your website. So it increases traffic to your website;
- You're one step ahead of the big players.
A great example of local SEO is, of course, the closest restaurant to eat out or pick up food from.
But it can also be a physical store or a professional painting company.
Google believes local SEO is becoming increasingly important. More and more, Google highlights local businesses in its search results.
Just type "order food," "painting company" or "online marketing agency" into Google.
You will see that lots of results pop up for businesses close to you.
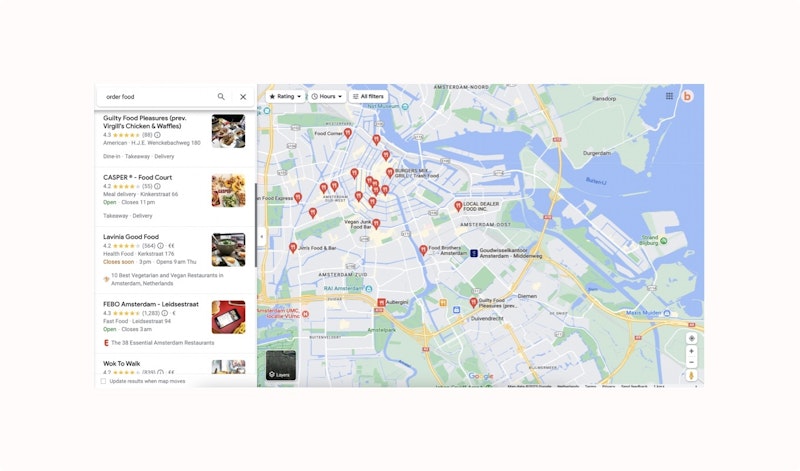
To be easy to find locally, there are several things to keep in mind:
- Set up a Google Business Profile;
- Use structured data to provide more information about your business;
- List your business in local business directories;
- Write local content for your website;
- Optimize Google Maps on your website;
- Acquire local backlinks.
We'll explain why each of these is important for local SEO.
Google Business Profile
Setting up a Google Business Profile is the best way to help locals find you.
This is where you enter numerous details, such as your company name, address details, website, and photos.
If you set this up completely and correctly, you’ll get a higher ranking for local searches.
In other words, if someone searches for your company name, a Google Business Profile with all your details will appear on the right side of the search results.
This works perfectly!
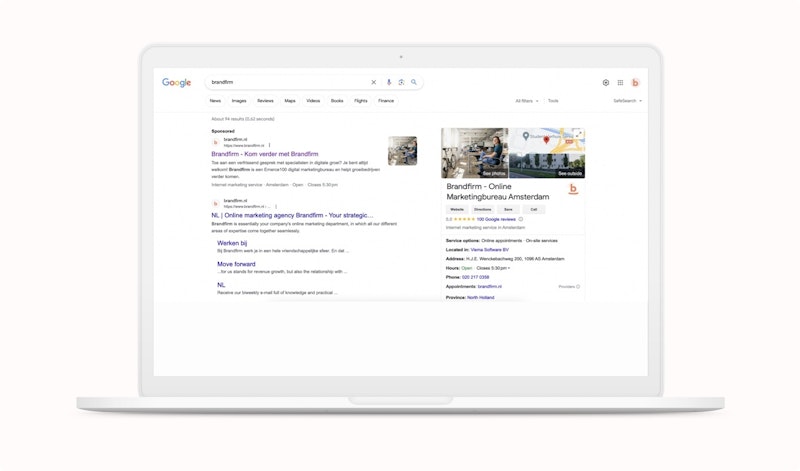
By the way, this doesn’t just happen when people search for your company name.
Related searches can also result in your company name appearing.
To give you an idea of a Google Business Profile, we included an example from Brandfirm below.
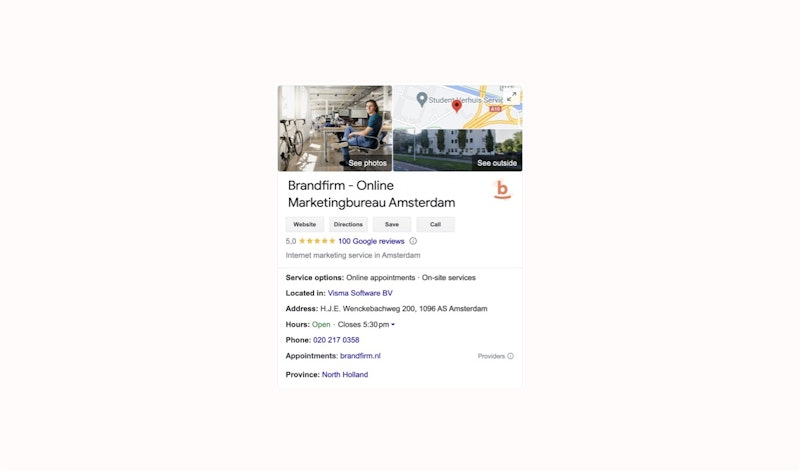
Adding structured data
We've mentioned structured data before, which means adding a piece of code to your content. Using schema.org, you can add structure to your data. This makes things even easier for Google.
Think about adding structured data to your:
- Address data;
- Phone number;
- Email address;
- Location name;
- Review stars.
Local business directories
Local directories want to provide an overview of businesses in a particular area.
There is a local business directory for every city, for instance.
By signing up, not only does Google find out more about your business, but people in the area do too.
On top of that, business directories also provide an extra link to your website. So great for link building!
Local content
With local content, think of landing pages specifically designed to mention local keywords.
Think 'Online marketing agency Amsterdam' or 'Painting company in Breda.'
But you can also capitalize on local search queries. Think "Where can I buy black pants in Haarlem?" or "Is there an SEO agency in the Veluwe area?"
To figure out the right search terms and queries, it's important to do keyword research.
You can find out more about keyword research in Chapter 4.
Google Maps
Google Maps is a great way to look up a company's address.
By placing a Google Maps map next to the contact information on your website, visitors can instantly see where you're located.
It also allows them to look up how far away you are.
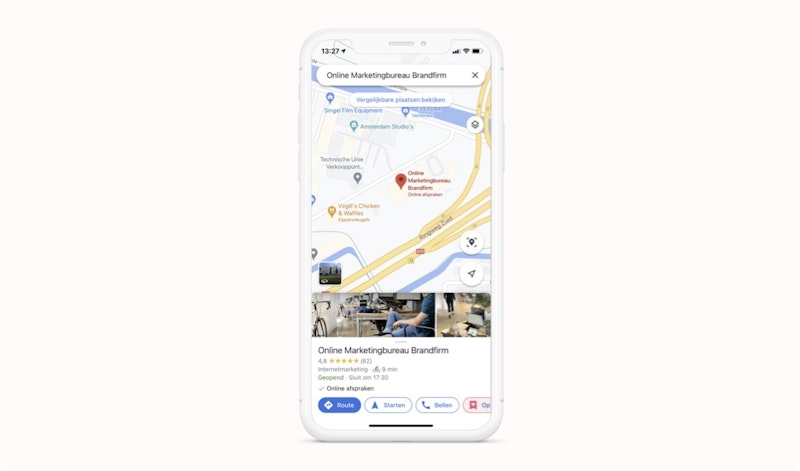
At the same time, a Google Maps map is an additional confirmation for the search engine. And this is beneficial for local SEO.
Local backlinks
In the heading 'local business directories,' we briefly mentioned link building.
Business directories are a great way to get backlinks, which benefits search engine optimization.
But there are also other ways, such as sharing content with other local businesses.
Consider an online newspaper or a local club.
Regional SEO
In addition to local SEO, there’s regional SEO.
Often, regional SEO is linked to local SEO. They have many similarities.
However, there is an important difference between the two forms of search engine optimization.
Whereas local SEO caters to a particular place (for example, Amsterdam), regional SEO relates to an entire region or area.
So in this case, not just Amsterdam, but a large part of North Holland.
This has several advantages for search engine optimization:
- You're not only visible in one city but in multiple areas. Using regional SEO, you can also target Haarlem, Alkmaar, and Den Helder, for example.
- By tailoring your content (such as landing pages) to multiple locations, you broaden the region where people can find you.
- You're visible to many more people because you're targeting a larger area. This drives more traffic and ultimately more customers.
International SEO
If your business attracts (or aims to attract) a foreign market, it’s wise to offer your website or webshop in multiple languages.
The most obvious is English, but you can also think about Spanish, French, or Chinese.
But just translating your website is not enough.
Your website must be optimized for search engines abroad. International SEO refers to making a foreign website easy to find, to appeal to the international market. But this requires a different approach.
There are several things you should look out for:
- Keep a good website structure. Consider new, international URLs and domains.
- Ensure proper SEO migration. This is important not to lose your authority. To do this, do thorough research on the current position and technology of your website.
- Adapt your content to your international target audience. This is different for each country. A French consumer will go for different searches than a Dutch consumer. So make sure you do keyword research for the relevant country and consumer.
- Take international search engines into account. Don’t just think of Google. Yandex, Baidu, Bing, and Yahoo! are also well-known international search engines. And these search engines have a vastly different algorithm than Google.
- Obtain international backlinks. A Spanish consumer won't have any use for an English backlink on a Spanish website. Again, consider the relevance and authority of the international backlink.
- Also consider local and regional SEO. This doesn't have to be the place your company is located. It can also be where there’s another branch, such as Paris or Curacao.
Summary
We went over local SEO, regional SEO, and international SEO in this chapter.
Local and regional SEO is particularly important if you want to be visible in a specific location or area.
International SEO is necessary if you want to operate in an international market.
But for this, you need to optimize your website and data in other ways.
Now that we’ve talked about the different aspects of SEO, it's time to decide what kind of SEO you’re going to use in your SEO strategy.
We'll explain this in the next chapter.
6. SEO strategy
A well-thought-out SEO strategy is the basis of an easy-to-find website.
Randomly applying different strategies or picking up an occasional element is counterproductive.
SEO requires quite some time but ultimately you'll have a great website.
And that's what we undoubtedly want.
In this chapter, we’ll show you the steps you need to take to develop a good SEO strategy.
Set goals
The first step to your SEO strategy is to set your goals.
What do you ultimately want to achieve? Consider:
- Increasing your online visibility;
- Attracting more relevant visitors to your website;
- Generating more sales.
Based on your goals, determine whether you can best achieve this with content optimization, technical SEO, or link building.
It's also key to see what areas you can improve.
Suppose your content is not well-written for your target audience.
It's important to tackle that first by optimizing the content optimization pillar. After that, you can tackle the technical SEO and link-building pillars of search engine optimization.
Make your goals measurable
Try to make your goals as measurable as possible.
For example, increasing your online visibility doesn't say much.
By when do you want to achieve that goal? And by what percentage do you want to increase your online visibility?
For example: you want to increase your online visibility by 50% within one year.
Do you find that after six months you've only increased your online visibility by 10%? You'll be able to make adjustments if that's the case.
We’ll explain how to measure your results in the next chapter.
Measuring results
There are several programs that will help you measure results.
The best-known are Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a program you can connect to your website or webshop to measure the following things:
- Target audience: who is visiting your website? Gain insights about the country of origin, the language they speak, what device and browser they use to visit your website, and whether visitors are new or returning.
- Acquisition: how are your visitors landing on your website? Consider direct traffic, organic or paid traffic, and social media traffic.
- Behavior: what are your visitors doing on your site? Think about which pages they visit, on which page they exit, and which page is most visited.
- Goals: what are they generating? Think conversions or money.
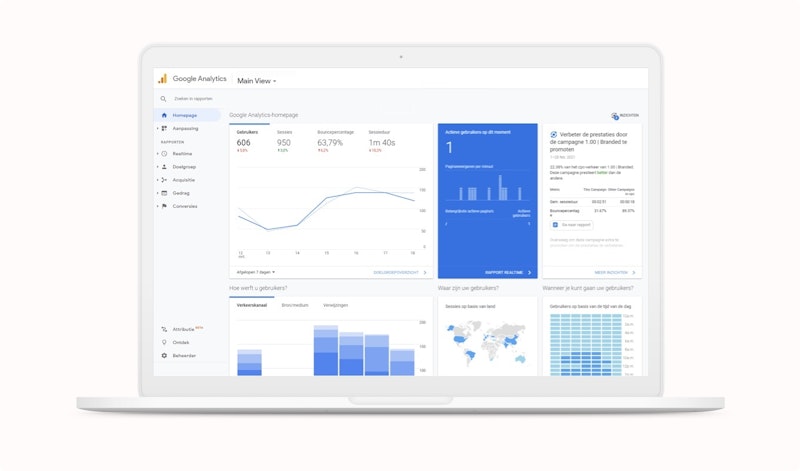
Google Analytics provides a good picture of what is happening on your website regarding search engine optimization.
With the help of this program, you can easily track your goals and make adjustments where necessary.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console has other functions. But it can be linked to Google Analytics.
With Search Console, you can track the performance and positioning of your website on Google.
Search Console helps you gain more insight into Google's search functionality. It also makes sure that your website is better indexed.
Google Search Console gives you the following data:
- Overview: the performance of your website in Google Search.
- Performance: all statistics about your website related to Google’s search results.
- URL inspection: information about certain URLs related to crawling and indexing.
- Index: the status of indexation (Coverage) and the Sitemap of your website.
- Optimizations: measures how mobile-friendly your website is.
- Security issues and manual fixes.
- Links: the sites that link to your website.
In short, Google Search Console and Google Analytics are two great programs to gain a clear and practical overview of your performance and other opportunities.
Identify opportunities
Are you not visible for an important keyword? Is traffic to your website slow? Do you notice that visitors in a certain region are not coming across your website? Or are there other results where you see opportunities?
Then take advantage of them. Especially if they relate to your goals.
For example, are you located in South Holland, but notice that there are very few visitors from that region? Or do you notice that you only have a few backlinks, even though your goal was to focus on the authority pillar of search engine optimization?
You can use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to analyze these results and identify opportunities accordingly.
7. SEO trends for 2024
SEO wouldn't be SEO if it didn't constantly optimize.
There are SEO trends for 2024 that Google is moving toward. In this section, we’ll highlight 4 SEO trends for 2024.
1 Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals is now an important ranking factor in Google’s algorithm. Core Web Vitals was included in May 2024.
We mentioned this briefly at the beginning of this guide, but here we’ll go into a bit more detail.
Core Web Vitals consists of:
- Largest Contentful Paint
- First Input Delay
- Cumulative Layout Shift
Largest Contentful Paint
This measures the loading performance observed on the pages of your website.
It calculates the time it takes for the largest element to appear.
For many websites, this is the header as it’s an image or video.
Does the LCP take more than 2.5 seconds to load? Then you had better reduce the load time. The limit set by Google is in fact 2.5 seconds.
This sounds fast, but ask yourself: would you mind waiting longer than 2.5 seconds for a website to load?
You probably would. And Google notices that trend, too.
First Input Delay
The time between a page loading and a moment of interaction is called the First Input Delay (FID).
Interaction includes, for example:
- Clicking on buttons;
- Clicking on a menu header;
- Filling out forms.
For the FID, Google has a limit of 100 ms, which is a good performance. Anything over 300 ms is considered poor.
Cumulative Layout Shift
The Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures the time between a page appearing on your screen and a layout shift.
These are observable layout changes.
Think of elements that take longer to load, such as images, ads, or special fonts.
Especially for mobile devices, this is considered a very important metric.
2 Google Passage Ranking
You can consider Google Passage Ranking to be a featured snippet 2.0, something we mentioned earlier.
It works like this: someone on a mobile device who’s looking for an answer will start typing that question into Google.
A Passage Ranking is a snippet of text from a particular website that provides an answer to that question.
Whereas with a featured snippet Google looks at the relevance of an entire page, Google Passage Ranking looks at the relevance of a particular paragraph of a page.
Of course, the relevance of an entire page is still going to be important.
3 Visual Search
Visual Searches are not yet a game-changer in the SEO world, but by 2024, it's sure to take a huge leap.
The term effectively describes what it is: searching for something by means of a visual image.
Think of that plant in your living room for which you can't remember the name. Or a piece of clothing and you’re dying to know what store sells it.
You can do visual searches on Pinterest. If you don't use this platform, you can use Google Lens. Upload or take a picture and you’ll find that Google will give you instant results.
4 SERP Features
It’s getting more and more difficult to stand out in the SERP, otherwise known as the results page on Google.
This is because the organic (non-paid) search results are being snowed under by SERP Features.
Think about:
- Reviews
- Ads
- Images or videos
- Products
- Music and podcasts
- Google Passage Ranking
- Local services
As a result, it’s even more important to stand out in the organic search results. You can do this by:
- Including an important keyword in your URL;
- Adjusting your meta title and meta description manually. Capitalize on feelings and emotions, for example;
- Adding rich snippets. Think of a recipe, podcast, or review;
- Adding visual content, such as videos, and photos.
8. Conclusion
After reading this guide, you can safely conclude that search engine optimization (SEO) doesn't happen overnight.
Search engine optimization consists of different pillars and types. Each type has a different purpose, so you need to carefully consider which type fits your SEO strategy.
Yet the different types of SEO also reinforce each other.
For example, content optimization and the use of the right keywords bring you closer to your target audience.
But depending on your target audience, you will also need to work with local, regional, or international SEO. And that again requires a lot of technical SEO, such as structured data and a proper URL structure.
On top of that, search engine optimization is constantly changing.
We need to take into account trends and developments in SEO.
For example, it's helpful to integrate Core Web Vitals and optimize your content to qualify for Google Passage Ranking.
Only by keeping up with trends will you secure a spot on the first page of the SERP.
We're curious about your take on search engine optimization. Why do you want to use SEO, and which form of search engine optimization best suits your goal?
Let us know by commenting on this guide! As a digital agency in Amsterdam we are happy to help you with SEO!
Advies over jouw SEO-strategie?
- Een gratis analyse t.w.v. 4 tot 6 uur werk
- Heldere SEO-strategie op maat
- 87% van de bedrijven die we analyseren loopt omzet mis

